In case of divergent insertion directions we have to parallelize for incorporating the bridge. This can be done either through a compensation-telescope or a sectioning-attachment.
This bridge was not subdivided about the balance of abutment divergences. Rather, the last crown had de–cemented in the past.
Likewise, it may be advisable to insert bridge divisions to compensate for the intrinsic mobility of the lower jaw in itself or to compensate for the different kinetics or mobility in the splinting of implants with natural teeth.
The attachment or Telskop is attached to the first structure that will be cemented (bridge or crown) and aligned with the insertion of the participating secondary structure, which is cemented thereafter. It has an omega-milling to a safe physical fixation and in order to prevent deflection or a decoupling of the structures.
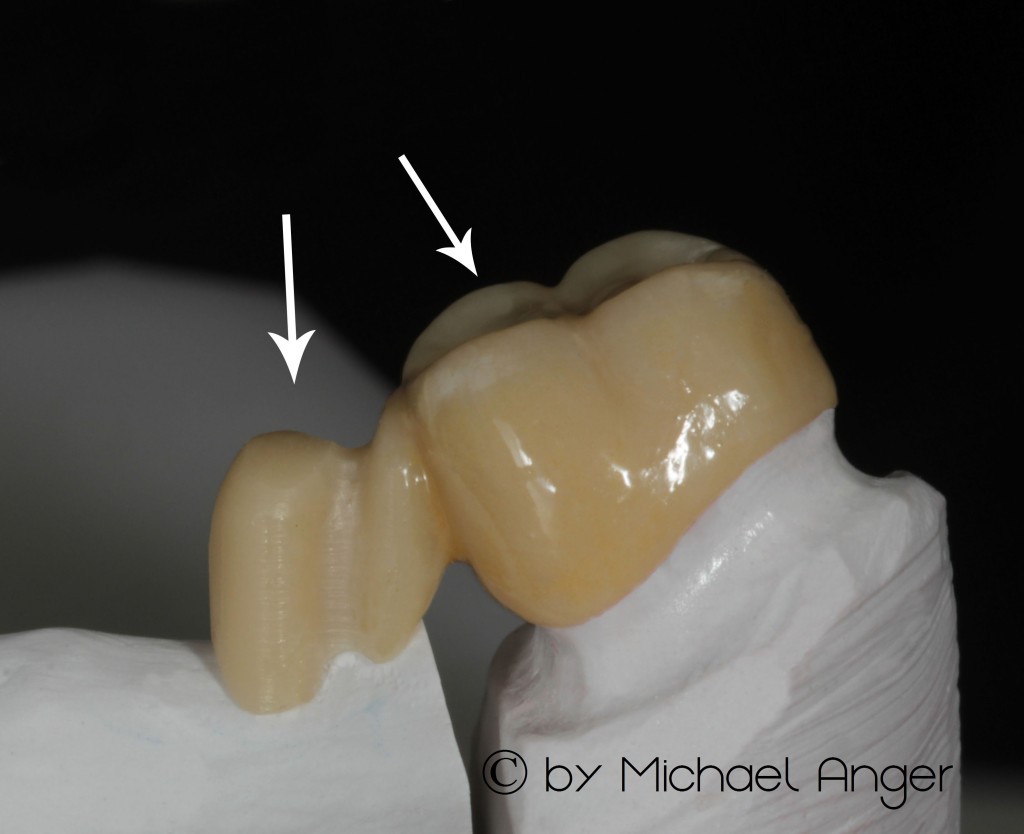
In these images, so we see the patrix of the attachment mounted mesial on the wisdom tooth, which will be first cemented . The matrix at the bridge structure is not cemented in this case on the primary part, but remains as a movable compound and as a support for the bridge-elements.
In the basal view of the bridge, the Omega–milling is easy to recognize. This prevents that the rear abutment tooth can be pushed posteriorly.
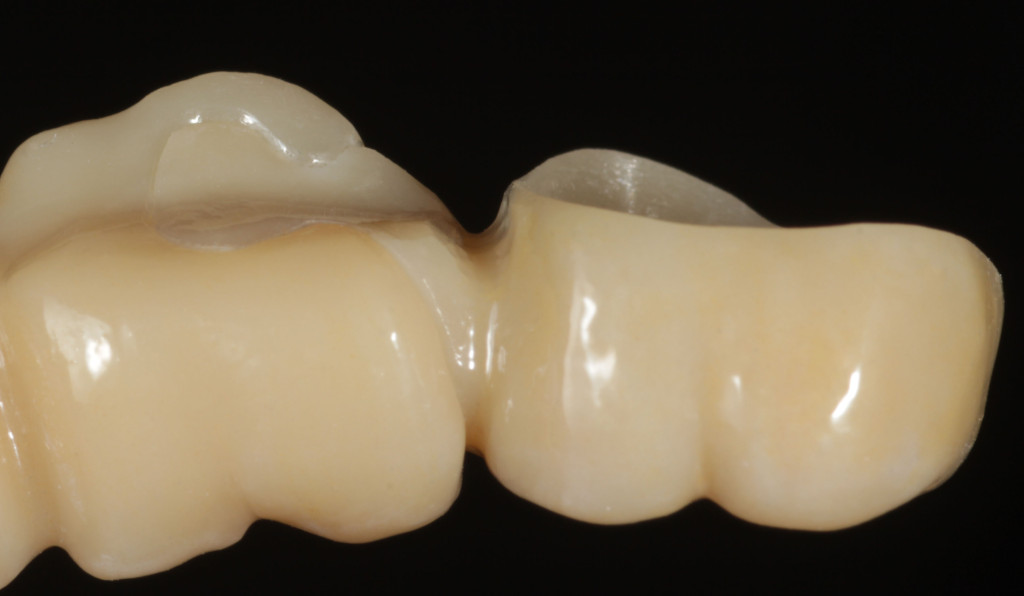
The occlusal support should be effected necessarily as close as possible to the rear crown. Above the bed load–pin some space should be left no tipping movement to exert pressure on the abutment tooth, as well as to avoid overloading of the attachment and a fraction.
In this picture we see the functioning of the attachment during assembly. The pin engages into the opening and the support is provided both on the inclined shoulder surfaces, as well as close to the crown.
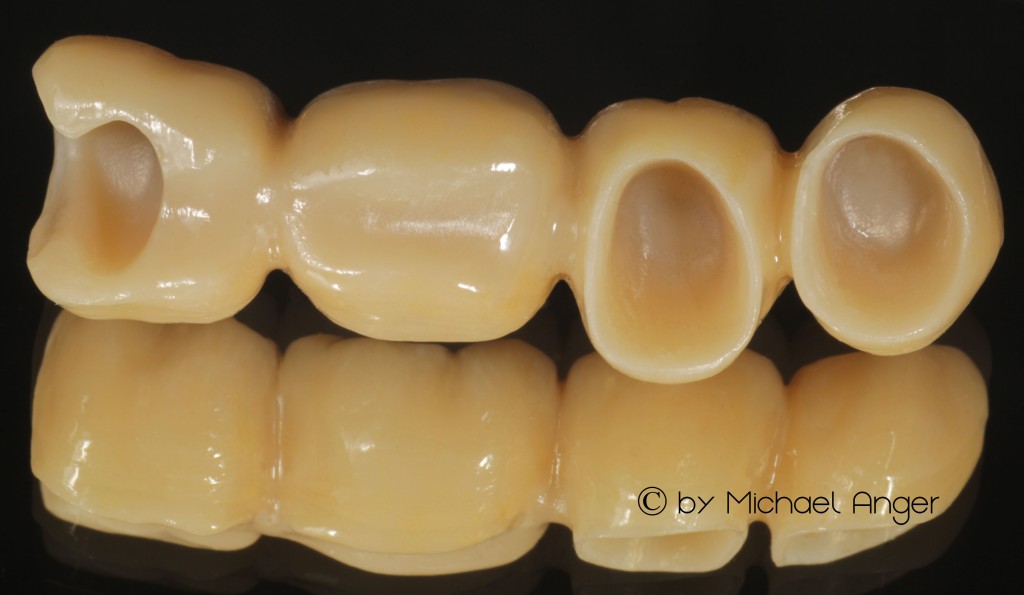
In the position of complete addition of primary and secondary part, both parts should fit without gaps.
The milling is carried out here with 2 °. This enables friction–free incorporation.
To the overviews :
 Your independent e-learning & support platform!
Your independent e-learning & support platform!